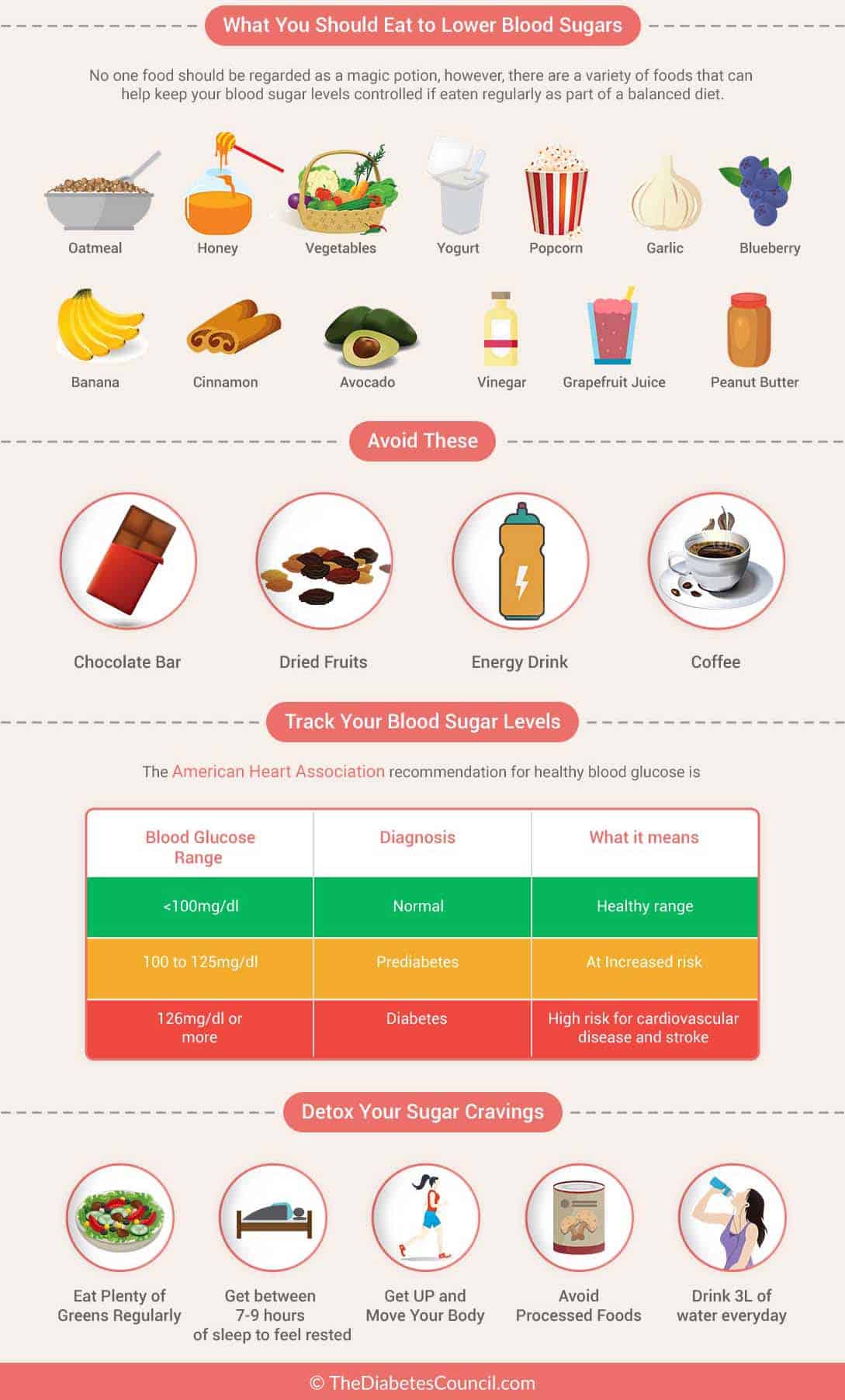
Uncontrolled blood sugar during pregnancy increases your risk of developing gestational diabetes, a potentially serious condition that can complicate delivery, according to the national institutes of health, and even increase your child's risk of developing type-2 diabetes later in life.. The goal during pregnancy is to keep the blood sugar as close to normal as possible without frequent or severe hypoglycemia. in general, keeping the blood sugar below 140 mg/dl (7.8 mmol) at the post-meal peak greatly reduces the risk for fetal macrosomia.. Whether you have diabetes prior to getting pregnant or have gestational diabetes as a result of pregnancy, the key to managing your condition remains the same: keeping your blood sugar under control. doing so can avoid the symptoms of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), including headaches, fatigue, loss of concentration, and blurred vision..
Gestational diabetes is a temporary condition that can occur during pregnancy. if you have gestational diabetes, it means you have higher blood sugar levels than normal during pregnancy.. During pregnancy, your body makes more insulin to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, but sometimes you don�t produce enough. gestational diabetes may cause your baby to have breathing difficulties, jaundice, low blood sugar and obesity later in life.. Do check blood sugar regularly to decrease diabetes complications �in order to decrease the risk of complications from gestational diabetes, close monitoring of fasting and postprandial.
No comments:
Post a Comment